Introduction
PEST Analysis is a strategic analytical tool used to evaluate the impact of external macro-environmental factors on an organization or industry. It helps identify opportunities and threats by analyzing Political, Economic, Social, and Technological factors. This tutorial will walk you through the PEST Analysis process using a case study of the Automotive Technology and Infrastructure Development Sector.
Benefits of PEST Analysis:
- Strategic Decision Making: PEST Analysis helps organizations make informed strategic decisions by providing a clear understanding of the external environment and its potential impacts.
- Opportunity Identification: By analyzing trends and shifts in the macro-environment, PEST Analysis can help identify new opportunities for growth and innovation.
- Risk Mitigation: Identifying potential threats enables organizations to develop contingency plans and mitigate risks associated with external factors.
- Stakeholder Management: Understanding the perspectives and expectations of various stakeholders (e.g., customers, investors, regulators, employees) helps build stronger relationships and improve communication.
- Long-term Planning: PEST Analysis helps organizations develop long-term plans by considering how external factors may evolve over time.
- ** Competitive Advantage:** By gaining insights into the macro-environment, organizations can make data-driven decisions to gain a competitive edge in the market.
- Resource Allocation: PEST Analysis helps allocate resources effectively by prioritizing areas that present the most significant opportunities or threats.
- Informed Communication: Understanding the external environment enables better communication with stakeholders, both internally (e.g., employees) and externally (e.g., customers, investors, regulators).
When to Use PEST Analysis:
- Strategic Planning: PEST Analysis is an essential component of strategic planning processes, helping organizations understand their operating environment and set long-term goals.
- Market Entrance or Expansion: When entering new markets or expanding existing ones, PEST Analysis helps assess the macro-environmental factors that may impact the organization’s performance.
- Business Model Innovation: PEST Analysis can identify shifts in the macro-environment that may necessitate changes in the business model, such as new customer preferences, regulatory changes, or technological disruptions.
- Risk Assessment: PEST Analysis helps identify risks associated with external factors, enabling organizations to develop contingency plans and crisis management strategies.
- Policy Formulation: For government entities and non-governmental organizations (NGOs), PEST Analysis can help inform policy decisions by understanding the macro-environmental context.
- Investment Decisions: Investors use PEST Analysis to evaluate the potential impact of external factors on the performance of companies they invest in or plan to invest in.
- Marketing and Product Development: PEST Analysis helps marketing teams understand consumer trends and preferences, and product development teams identify new opportunities for innovation.
- Periodic Review: Regularly updating PEST Analysis ensures that organizations remain adaptive and responsive to changes in the macro-environment, helping maintain a competitive edge.
When NOT to Use PEST Analysis:
- Operational Decisions: PEST Analysis focuses on external macro-environmental factors, making it less suitable for operational decisions that rely more on internal data and processes.
- Short-term Decision Making: While PEST Analysis can help identify immediate threats and opportunities, it is best suited for long-term decision-making due to its focus on trends and shifts in the macro-environment.
- Industry-specific Factors: PEST Analysis primarily addresses external macro-environmental factors; industry-specific factors, such as competitive dynamics or regulatory changes specific to the industry, may require additional analysis, such as Porter’s Five Forces or Industry Analysis.
In summary, PEST Analysis is a versatile tool that can support various decisions and planning processes. Its primary value lies in helping organizations understand and navigate the external macro-environment, enabling them to make informed decisions, identify opportunities, and mitigate risks.
Step 1: Understand the PEST Factors
- Political Factors: Government regulations, policies, and actions that may impact the organization or industry.
- Economic Factors: Economic conditions, trends, and shifts that can influence the organization’s performance.
- Social Factors: Societal trends, demographics, and cultural shifts that may affect the organization’s customer base or operations.
- Technological Factors: Technological advancements, trends, and disruptions that can create new opportunities or threats.
Step 2: Gather Information
Collect relevant data and information about each PEST factor from various sources such as:
- Industry reports and publications
- Government websites and documents
- News articles and media reports
- Market research studies
- Social media trends and discussions
Step 3: Analyze Each PEST Factor
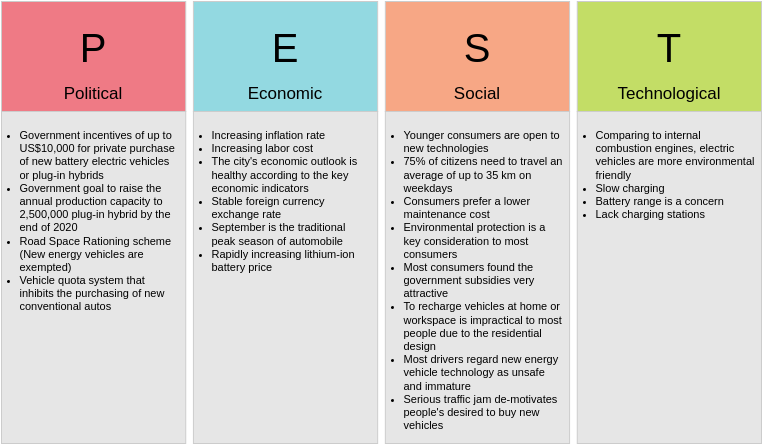
1. Political Factors
- Government Incentives: Incentives like tax credits and subsidies encourage the adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) and promote sustainable transportation.
- Production Goals: Targets for EV production capacity, such as China’s goal of 2,500,000 plug-in hybrids by 2020, drive investment in EV manufacturing.
- Energy Policies: Policies aimed at reducing reliance on fossil fuels and promoting renewable energy influence vehicle production and usage.
2. Economic Factors
- Inflation and Labor Costs: Increasing inflation leads to higher labor costs, impacting vehicle production costs.
- Energy Costs: Rising energy prices affect the affordability and profitability of manufacturing processes.
- Foreign Currency Exchange: Fluctuations in exchange rates can lead to increased costs for imported components and materials, impacting competitive pricing.
3. Social Factors
- Consumer Trends: Younger consumers prefer environmentally friendly and cost-effective vehicles, with weekday travel averaging around 35 km.
- Environmental Protection: Consumers increasingly consider environmental factors when purchasing vehicles, with government subsidies influencing their choices.
- Maintenance Costs: Consumers favor vehicles with lower maintenance costs, giving electric vehicles an advantage.
4. Technological Factors
- Wireless Energy Transmission: Advancements in wireless charging systems improve electric vehicle charging convenience and efficiency.
- Battery Technology: Improvements in battery range and charging speed enhance the viability of electric vehicles for everyday use.
- Charging Infrastructure: The availability and accessibility of charging stations are crucial for the adoption and growth of the EV market.
Step 4: Identify Opportunities and Threats
Based on the analysis, identify opportunities and threats for the automotive industry:
Opportunities:
- Government incentives and production goals drive demand for EVs.
- Consumer trends and preferences for eco-friendly, low-maintenance vehicles.
- Technological advancements in wireless charging and battery technology.
Threats:
- Economic factors like increasing labor costs, energy prices, and currency fluctuations can impact production costs and profitability.
- Social factors such as uncertain consumer preferences and potential changes in environmental concerns.
- Technological challenges like the need for improved charging infrastructure and further advancements in battery technology.
Step 5: Develop Strategies
Strategies should address both opportunities and threats. For example:
- Exploit opportunities by investing in EV production, improving battery technology, and expanding charging infrastructure.
- Mitigate threats by diversifying the supply chain to manage currency fluctuations, developing affordable EV models to combat increasing labor and energy costs, and monitoring consumer trends.
Step 6: Monitor and Review
Regularly update the PEST Analysis to ensure it remains relevant and accurate. Changes in political policies, economic trends, social shifts, and technological advancements can significantly impact the automotive industry, so continuous monitoring is crucial.
Using Mind Maps for PEST Analysis
Using a mind map to develop a PEST analysis is an ideal approach for several reasons:
1. Visual Clarity
- Simplifies Complex Information: Mind maps break down complex information into manageable chunks, making it easier to understand and analyze.
- Visual Representation: The visual nature of mind maps helps in quickly grasping the relationships between different factors.
2. Enhanced Organization
- Structured Layout: Mind maps provide a clear and structured layout, ensuring that all relevant factors are covered systematically.
- Easy Navigation: The hierarchical structure allows for easy navigation through different levels of information.
3. Improved Memory and Recall
- Visual Cues: The use of colors, images, and symbols in mind maps aids in better memory retention and recall.
- Associative Thinking: Mind maps encourage associative thinking, helping to link related concepts and ideas.
4. Flexibility and Adaptability
- Dynamic Tool: Mind maps are flexible and can be easily updated as new information becomes available.
- Customizable: They can be customized to fit the specific needs of the analysis, allowing for the inclusion of additional branches or sub-branches as required.
5. Enhanced Creativity and Brainstorming
- Encourages Creativity: The free-form nature of mind maps encourages creative thinking and the exploration of new ideas.
- Brainstorming Tool: Mind maps are excellent for brainstorming sessions, allowing for the quick capture of ideas and their organization into coherent categories.
6. Collaboration and Communication
- Collaborative Tool: Mind maps can be easily shared and collaborated on, making them ideal for team-based analysis.
- Effective Communication: They provide a clear and concise way to communicate findings and insights to stakeholders.
7. Holistic View
- Big Picture Perspective: Mind maps provide a holistic view of the analysis, showing how different factors interconnect and influence each other.
- Comprehensive Analysis: They ensure that all aspects of the PEST analysis are considered, leading to a more thorough and comprehensive understanding.
Steps to Conduct PEST Analysis Using a Mind Map
- Start with the Central Node:
- Create a central node labeled “PEST Analysis” in your mind map. This will be the starting point from which all other branches will extend.
- Create Four Main Branches:
- From the central node, draw four main branches labeled “Political,” “Economic,” “Social,” and “Technological.” These represent the four categories of the PEST analysis.
- Add Sub-branches for Each Factor:
- Under each main branch, add sub-branches to detail specific factors. For example, under “Political,” you might include sub-branches for government policies, tax regulations, trade restrictions, etc.
- Detail Each Sub-branch:
- Further expand each sub-branch with more specific details. For instance, under “Economic,” you might add sub-branches for inflation rates, unemployment rates, economic growth, etc.
- Use Keywords and Short Phrases:
- Keep the information concise by using keywords and short phrases. This makes the mind map easy to read and understand at a glance.
- Incorporate Visual Elements:
- Use colors, icons, and images to differentiate between the branches and make the mind map visually appealing. This can help in quickly identifying different factors and their impacts.
- Review and Update Regularly:
- A PEST analysis is not a one-time activity. Regularly review and update your mind map to reflect any changes in the external environment.
Key Concepts of PEST Analysis
- Political Factors:
- Government Policies: Regulations and policies that can affect the business environment.
- Tax Regulations: Tax policies that impact business operations and profitability.
- Trade Restrictions: Import/export restrictions that can affect supply chains.
- Economic Factors:
- Inflation Rates: The rate at which prices for goods and services rise, affecting purchasing power.
- Unemployment Rates: The level of unemployment which can influence consumer spending and labor availability.
- Economic Growth: The overall growth of the economy which impacts business opportunities.
- Social Factors:
- Demographic Changes: Changes in population size, age, and composition that can affect market demand.
- Consumer Preferences: Trends in consumer behavior and preferences that influence product demand.
- Cultural Attitudes: Societal values and attitudes that can impact business practices and marketing strategies.
- Technological Factors:
- Technological Advancements: Innovations that can create new opportunities or disrupt existing markets.
- Research and Development: Investments in R&D that can lead to new products and services.
- Automation and AI: The impact of automation and artificial intelligence on business processes and employment.
Example Mind Map Structure
Here’s a simplified example of how your mind map might look:
PEST Analysis
├── PoliticalPNG
│ ├── Government Policies
│ ├── Tax Regulations
│ └── Trade Restrictions
├── Economic
│ ├── Inflation Rates
│ ├── Unemployment Rates
│ └── Economic Growth
├── Social
│ ├── Demographic Changes
│ ├── Consumer Preferences
│ └── Cultural Attitudes
└── Technological
├── Technological Advancements
├── Research and Development
└── Automation and AI
Here’s a mind map structure for the PEST analysis of the automotive technology and infrastructure development sector:
PEST Analysis Mind Map
Political Factors
- Government Incentives
- Up to $10,000 for private purchase of EVs
- Production Goals
- 2,500,000 plug-in hybrids by end of 2020
- Energy Policies
- New policies affecting vehicle production
Economic Factors
- Inflation and Labor Costs
- Increasing inflation rates
- Rising labor costs
- Energy Costs
- Rising energy costs
- Foreign Currency Exchange
- Stable exchange rates
Social Factors
- Consumer Trends
- Younger consumers prefer EVs
- Average travel up to 35 km on weekdays
- Environmental Protection
- Key consideration for consumers
- Government subsidies influencing trends
- Maintenance Costs
- Preference for lower maintenance costs
Technological Factors
- Wireless Energy Transmission
- Advancements in EV charging stations
- Battery Technology
- Addressing range and charging speed concerns
- Charging Infrastructure
- Availability of charging stations
- Slow charging times
This mind map structure helps visualize the various external factors influencing the automotive industry.
Conclusion
PEST Analysis is an invaluable tool for understanding and navigating the macro-environmental factors influencing the automotive industry. By regularly analyzing Political, Economic, Social, and Technological factors, stakeholders can make informed decisions, anticipate trends, and capitalize on emerging opportunities.
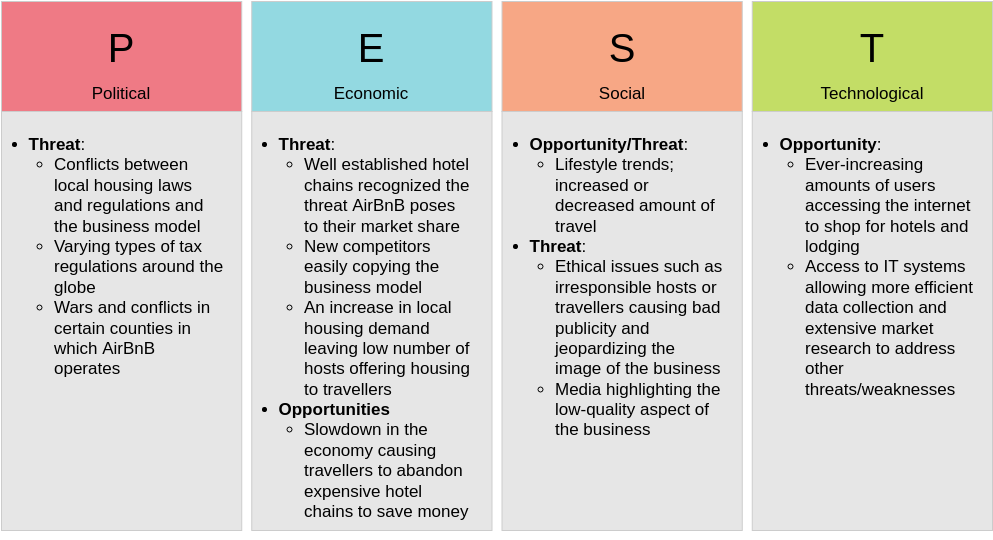
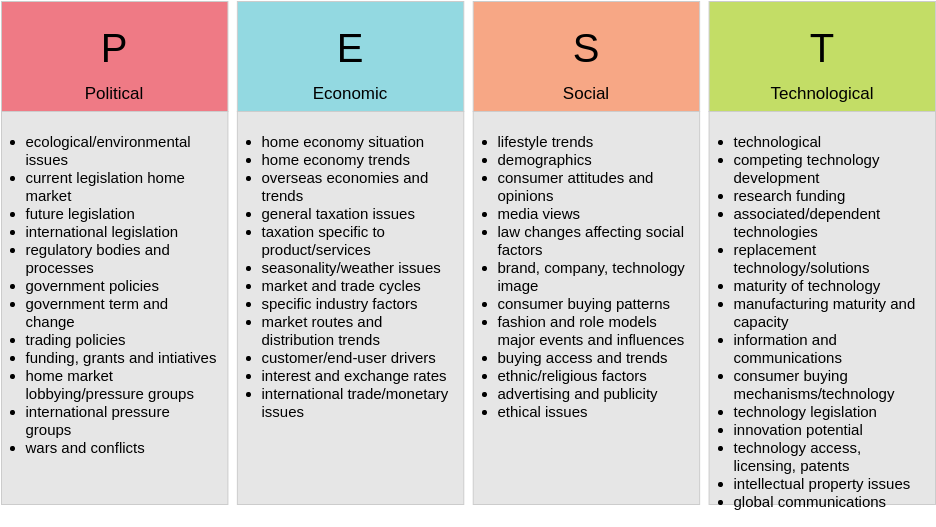
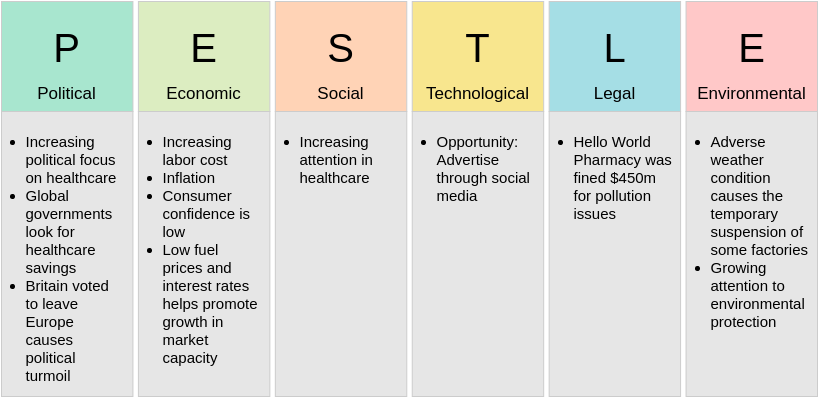
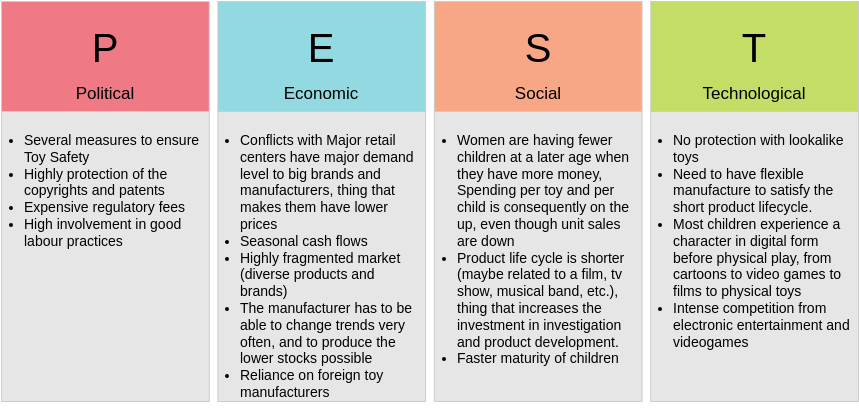
Pest Analysis – 5 templates